In this guide, we’ll explore what a cold chain is and why it’s crucial for transporting temperature-sensitive goods like food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Whether you're new to logistics or looking to improve your shipping processes, this article will help you understand the key components, challenges, and technologies involved in maintaining a reliable cold chain. Learn how efficient cold chain management ensures product quality and safety while saving costs.
What is Cold Chain Logistics?
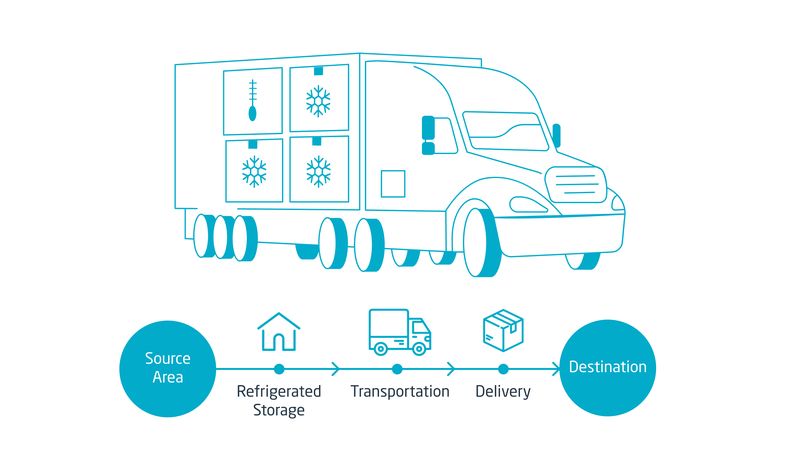
Cold chain logistics refers to the process of transporting temperature-sensitive goods in a controlled environment to maintain their required temperature throughout the entire supply chain. This type of logistics ensures that perishable products, such as food, pharmaceuticals, or even certain vehicle parts, are transported, stored, and handled at specific temperatures to prevent spoilage, degradation, or damage.
At its core, cold chain logistics involves the seamless transportation and storage of goods that need to be kept within a specific temperature range. This could include refrigeration or freezing at various stages of transport to ensure that products remain in optimal condition until they reach their final destination. In addition to refrigeration, cold chains often require specialized solutions such as gel packs, dry ice, liquid nitrogen, and insulated blankets to keep shipments at the correct temperature throughout their journey.
For example, when shipping perishable food items like fruits, vegetables, or meats, maintaining the right temperature is essential to prevent spoilage. In the case of vehicles, certain parts may require climate control to avoid deterioration or rust. This is where cold chain logistics plays a crucial role.
A cold chain typically includes refrigerated trucks, containers, warehouses, and even ships or planes designed to maintain the required temperatures. These controlled environments ensure that goods are safe, efficient, and ready for use when they arrive, without having been exposed to harmful temperature fluctuations.
History of Cold Chain Logistics
The concept of cold chain logistics has been around for centuries, but it has evolved significantly over time. The origins date back to the 18th century, when British fishermen developed methods to keep their catch cool. In the 19th century, reefer ships and railcars appeared, followed by the first cold store in London in 1882.
In the early 20th century, refrigerated railcars were introduced in the U.S. to keep fresh produce cool as it traveled across the country, making it possible for goods to be shipped long distances without spoiling. By the 1920s, advancements in refrigeration technology led to the development of refrigerated trucks, allowing food suppliers and distributors to reach remote or distant locations.
The first mobile refrigeration truck was patented in the 1930s in the U.S., and by the 1950s, refrigerated trucks and trains enabled long-distance food distribution. With the rise of air travel in the mid-20th century, refrigerated air cargo began to take shape, enabling goods like pharmaceuticals, medical supplies, and even sensitive electronics to be shipped globally without the risk of temperature fluctuations.
Today, cold chain logistics is a highly sophisticated industry, utilizing specialized containers, sensors, and monitoring systems that ensure products are transported safely and efficiently. The industry has major economic significance: it is a multi-billion-dollar sector that provides thousands of jobs across agriculture, manufacturing, and retail. At the same time, it faces sustainability challenges, since refrigeration consumes a lot of energy and refrigerant gases impact the climate. To address this, companies are innovating with energy-efficient facilities, low-impact refrigerants, and alternative-fuel vehicles.
Industries That Rely on Cold Chain
Cold chain logistics plays a critical role in a variety of industries that rely on the safe transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive goods. From life-saving medicines to fresh produce, many products need to be kept at precise temperatures to maintain their quality and safety. Below, we explore the key industries that depend heavily on cold chain logistics.
Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the most significant sectors that depend on cold chain logistics. Temperature-sensitive medicines, including vaccines, biologics, and certain injectable drugs, must be stored and transported at specific temperatures to remain effective and safe for use. Vaccines require very strict cold chain standards, often between +2 °C and +8 °C, and sometimes ultra-cold storage. National health authorities mandate full compliance with these requirements. Immunization providers must go through cold chain accreditation, showing that they have proper monitoring systems and equipment in place. Updates also include guidance that pharmaceutical refrigerators older than 10 years can still be used if continuous real-time monitoring and alarm systems are installed. Community pharmacies offering vaccinations are also required to follow cold chain standards, with appropriate equipment, monitoring, and documentation. Immunization coordinators support them with equipment advice, breach management, and compliance checks.
For example, vaccines often require refrigeration between 2°C and 8°C to ensure their potency. If the temperature fluctuates too much during transportation, the vaccine could lose its effectiveness, putting patients at risk. The cold chain helps prevent this by using refrigerated trucks, air transport, and temperature-controlled warehouses to ensure the drugs are kept within their required temperature ranges at all times.
Other pharmaceutical products, such as gene therapies, proteins, and monoclonal antibodies, also require stringent temperature control. The integrity of these products can be compromised if exposed to heat or cold beyond their specified range, making the cold chain an essential part of the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Food and Beverages
The food and beverage industry is perhaps the most obvious user of cold chain logistics. Many food products, particularly perishables like fruits, vegetables, dairy, meat, and seafood, need to be kept at precise temperatures to prevent spoilage and preserve freshness.
For example, seafood must be kept frozen or refrigerated to maintain its quality and prevent bacterial growth. Similarly, fresh produce like berries and leafy greens need to be stored in cool environments to slow down ripening and keep them fresh during transport. Dairy products such as milk and cheese must also be kept at cold temperatures to prevent spoilage.
The cold chain ensures that these products remain safe for consumption and retain their quality from farm or factory to retail store or restaurant. From refrigerated trucks to cold storage warehouses and even specialized refrigerated containers for sea freight, the cold chain is the backbone of global food distribution, enabling consumers to access fresh products from all over the world.
Chemicals
Certain chemicals, including those used in industrial manufacturing, research, and even consumer goods, require temperature-controlled environments to maintain their stability and effectiveness. These chemicals can range from temperature-sensitive solvents and adhesives to specialty coatings and paints.
For example, many chemicals have a limited shelf life and can degrade or react unpredictably if stored at the wrong temperature. Flammable chemicals may become volatile if exposed to heat, while others may solidify if they’re kept too cold. The cold chain ensures that these products are stored and transported at the right temperatures to avoid safety risks and preserve their chemical properties.
In the case of high-performance coatings or industrial adhesives, temperature control is crucial to prevent the products from hardening or losing their effectiveness during transport. The cold chain helps safeguard these materials during transit, ensuring that they arrive at their destination in usable condition, ready for processing or application.
Other Industries Benefiting from Cold Chain Logistics
While pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and chemicals are the primary industries relying on cold chain logistics, other sectors also benefit from temperature-sensitive transport. These include:
- Floral Industry: Flowers and plants are often transported under controlled temperatures to prevent wilting or damage during transit.
- Cosmetics: Certain cosmetic products, particularly those containing active ingredients, may need to be stored at cooler temperatures to maintain their effectiveness and texture.
- Electronics: Some sensitive electronic components, like semiconductors, may require temperature control to prevent damage during transport.
Components of a Successful Cold Chain
A successful cold chain relies on a seamless integration of various components that work together to ensure that temperature-sensitive goods are transported and stored safely. From the point of origin to the final destination, every step in the cold chain must be carefully managed to maintain the required temperature range. Below are the key components of a successful cold chain: warehousing, transportation, and monitoring systems.
Warehousing
Warehousing plays a crucial role in cold chain logistics, as it serves as a temporary storage solution before products are transported to their next destination. Cold storage warehouses are specifically designed to keep products at the right temperature and humidity levels, preventing spoilage or degradation.
These warehouses are equipped with refrigeration systems that are capable of maintaining a consistent temperature, whether it’s a deep-freeze environment for frozen goods or a refrigerated environment for products like dairy, fruits, or pharmaceuticals. In addition to refrigeration, some cold storage facilities also feature climate-controlled rooms to regulate humidity, which is essential for preserving certain products. Beyond vehicles and warehouses, cold chain logistics also relies on insulated packaging such as foam boxes, gel packs, and liners to maintain temperature inside containers during shipping.
The key to a successful cold chain warehouse is its ability to monitor temperature fluctuations and respond quickly if issues arise. A well-managed cold storage facility will have backup power systems, regular maintenance schedules for refrigeration units, and systems in place to ensure that all goods remain within their designated temperature range.
For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, cold storage is critical for preserving the potency of vaccines, which must be stored between 2°C and 8°C. A malfunctioning refrigeration unit or power failure could compromise the entire batch of vaccines, making it essential for warehouses to have robust temperature monitoring and backup systems in place.
Transportation
Transportation is another essential component of the cold chain, as it involves moving temperature-sensitive products from one location to another. This can include road transport, air freight, sea shipping, or rail transport, with each mode requiring specific methods to maintain a controlled temperature environment.
Refrigerated trucks are commonly used for road transport, providing the flexibility to transport goods to and from distribution centers, retail locations, or directly to consumers. These trucks are equipped with advanced refrigeration units to ensure the temperature is regulated throughout the journey.
In air transport, cold chain shipments are typically placed in specially designed temperature-controlled containers or cargo holds to maintain the desired temperature. Air transport offers speed, making it ideal for shipping high-value or time-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals, across long distances.
Sea freight and rail transport also play a key role in cold chain logistics, especially for bulk shipments of perishable goods. Refrigerated containers (also known as "reefers") are used to transport products like fruits, vegetables, meat, or seafood by sea. These containers are equipped with their own cooling systems to maintain the required temperature for the duration of the voyage.
Regardless of the mode of transportation, it is essential that temperature-controlled vehicles or containers are regularly monitored to ensure that temperatures remain stable throughout the journey. Drivers and crews must be trained in cold chain procedures to avoid mishandling products or allowing the temperature to rise or fall outside the designated range.
Monitoring Systems
Monitoring systems are the backbone of a successful cold chain, as they provide real-time data on the temperature and condition of products during transport and storage. These systems use a variety of sensors, GPS trackers, and cloud-based software to continuously monitor the environment and ensure the integrity of temperature-sensitive goods.
There are two main types of monitoring systems used in cold chain logistics: active monitoring and passive monitoring.
-
Active Monitoring: This system uses sensors that continuously track temperature, humidity, and even location during transportation. These sensors transmit data to a central system or cloud platform, allowing logistics managers to monitor the status of goods in real-time. If the temperature moves outside the acceptable range, the system can send an alert, prompting immediate action, such as adjusting the refrigeration unit or rerouting the shipment.
-
Passive Monitoring: Unlike active systems, passive monitoring relies on data loggers or indicators that record temperature data at set intervals. These devices are placed within the cargo and can be reviewed after the shipment has been completed. While passive monitoring does not provide real-time alerts, it is still an essential tool for validating the condition of goods upon arrival and assessing the overall reliability of the cold chain process.
Both types of monitoring systems help ensure that goods remain within the required temperature range and provide a traceable record of temperature history, which is particularly important in industries such as pharmaceuticals or food safety. For example, if a batch of vaccines arrives at its destination and is found to have been exposed to temperatures outside the required range, the monitoring system will help identify the cause and determine if the product is still safe to use.
Challenges in Maintaining Cold Chain Integrity
Maintaining the integrity of a cold chain is no easy task, as even small disruptions can lead to spoilage, degradation, or safety risks. The main challenges include:
- Temperature fluctuations: These can result from transport delays, improper handling during loading/unloading, or extreme weather. Even small deviations can compromise pharmaceuticals or reduce the shelf life of perishable foods.
- Equipment failures: Malfunctions in refrigeration units, compressors, or monitoring systems can cause rapid temperature changes. Without maintenance, risks increase — e.g., faulty seals, dirty filters, outdated software.
- Infrastructure and visibility: High costs of building reliable cold chain infrastructure, combined with poor visibility across global supply chains, increase the risk of failure.
- Human error: Mistakes in handling, such as leaving doors open or ignoring alarms, can quickly compromise the cold chain.
These challenges highlight why cold chain logistics requires both advanced technology and skilled management.
How to Mitigate Cold Chain Challenges
To reduce risks and ensure product safety, cold chain operators implement several strategies:
- Advanced monitoring systems: Real-time sensors track temperature, humidity, and location, sending alerts for immediate intervention.
- Regular equipment maintenance: Scheduled checks prevent malfunctions and extend the life of refrigeration units.
- Contingency planning: Backup power systems, portable refrigeration, and rerouting strategies help avoid disruptions.
- Employee training: Proper training minimizes human error and ensures protocols are followed.
In addition to addressing risks, cold chain management provides key advantages: it extends shelf life, ensures safer food by reducing bacterial growth, and gives companies a competitive edge by enabling long-distance distribution of high-quality perishables.
Technologies Used in Cold Chain
Cold chain logistics has evolved significantly with the advancement of technology, making it possible to transport temperature-sensitive products safely and efficiently. To ensure that perishable goods such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals remain in optimal condition throughout their journey, several technologies are employed. These include IoT sensors, reefer containers, and GPS tracking. Let’s take a deeper dive into these technologies and how they help maintain the integrity of the cold chain.
Real-Time Temperature Monitoring with IoT Sensors
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized cold chain management by providing real-time monitoring and data collection. IoT sensors are embedded in refrigerated trucks, containers, and storage units, continuously measuring temperature, humidity, and even pressure. These sensors send data to centralized systems, where logistics managers can monitor shipment conditions at every step.
For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, vaccines must be kept within a specific temperature range to remain effective. IoT sensors track this in real time, sending alerts if the temperature deviates from the required range. This allows immediate corrective action, such as adjusting the cooling system or rerouting the shipment to a facility with better conditions.
One of the key advantages of IoT sensors is their ability to generate detailed, time-stamped data that proves goods were kept within the correct temperature range throughout transport. This is invaluable for regulatory compliance and helps identify recurring issues, such as fluctuations linked to specific routes or equipment.
By integrating IoT monitoring into best practices, businesses can ensure the integrity of their shipments and comply with strict standards for pharmaceuticals and food. If a malfunction occurs in the cooling system, real-time monitoring triggers an alarm, enabling logistics managers to act quickly and prevent spoilage or product loss.
Reefer Containers
Reefer containers, or refrigerated containers, are one of the most critical technologies in cold chain logistics, particularly for long-haul transportation. These containers are designed to maintain a consistent temperature over extended periods, making them ideal for shipping perishable goods via sea, air, or land.
Reefer containers are equipped with built-in refrigeration units that allow them to be set to specific temperatures, whether it’s freezing, chilled, or ambient. They also feature insulation that helps minimize temperature fluctuations and maintain the internal environment. These containers come in various sizes, making them suitable for transporting everything from a small batch of pharmaceuticals to large quantities of food and beverages.
For example, when shipping seafood across the globe, reefer containers are essential to ensure that the temperature stays below freezing, preserving the freshness and quality of the fish during the long journey. Similarly, when transporting perishable fruits and vegetables, these containers help maintain an optimal environment by regulating the temperature and humidity levels to prevent spoilage.
One of the key advantages of reefer containers is that they can be used across multiple modes of transportation, such as trucks, ships, and airplanes. This flexibility ensures that temperature-sensitive goods can remain in a controlled environment, even as they switch from one transportation mode to another. Reefer containers are also equipped with tracking and monitoring systems, allowing logistics managers to oversee the condition of the goods inside during transit.
GPS Tracking in Cold Chain Logistics
GPS tracking is an essential technology that enables real-time location monitoring of shipments. It allows companies to oversee the exact position of temperature-sensitive cargo, helping ensure timely delivery and reducing the risk of delays or losses.
For instance, a pharmaceutical company transporting vaccines can track the shipment’s real-time location and estimated arrival, which is critical for coordinating storage and distribution. If there are delays caused by traffic or weather, the logistics team can reroute or adjust the delivery schedule to prevent temperature excursions.
GPS tracking also strengthens shipment security. Real-time data helps companies detect theft, route deviations, or prolonged stops, enabling immediate intervention.
Furthermore, GPS integrates with IoT sensors to provide a full view of both shipment location and condition. This combination ensures that products not only stay within the required temperature range but also arrive exactly where and when they are needed.
Integration of Technologies for Enhanced Cold Chain Management
The integration of IoT sensors, reefer containers, and GPS tracking systems has dramatically improved cold chain management by providing a more cohesive and transparent supply chain. These technologies work together to provide end-to-end visibility, allowing companies to monitor both the environmental conditions and the location of their shipments in real time.
For example, if an IoT sensor detects a temperature deviation in a reefer container, the GPS system can quickly pinpoint the location of the shipment and help logistics managers identify potential causes of the issue. Whether it’s a malfunction in the refrigeration unit, a delay in transit, or a route deviation, the combined data from these technologies enables faster decision-making and quicker resolution of problems.
This level of visibility and control helps improve the overall reliability and efficiency of the cold chain. It also provides peace of mind for customers, knowing that their temperature-sensitive goods are being carefully monitored and protected throughout the entire journey.
Best Practices for Shipping Perishable Items
Shipping perishable items, whether it’s fresh produce, seafood, meat, or pharmaceuticals, requires meticulous planning and attention to detail to maintain their quality, safety, and integrity during transit. Perishable goods are sensitive to changes in temperature, humidity, and handling conditions, and any disruptions in the supply chain can lead to spoilage or damage. To ensure that these items arrive at their destination in optimal condition, businesses must follow best practices for shipping perishables. Below, we will outline key strategies to effectively transport these goods.
1. Proper Packaging for Temperature Control
The first and most crucial step in shipping perishable items is ensuring that the packaging is designed to maintain the required temperature. Temperature-sensitive goods should be packaged in insulated containers or boxes to reduce the impact of external temperature fluctuations. These containers should include gel packs, dry ice, or ice packs to maintain a cool temperature during transit.
For example, when shipping fresh seafood, it is essential to pack the fish in insulated boxes with gel packs or dry ice, ensuring they stay frozen throughout the journey. Similarly, when transporting vaccines, special packaging such as thermal blankets or refrigerated coolers can help maintain the appropriate temperature range for the product.
The packaging should also be durable to withstand rough handling during transportation, as fragile packaging can lead to product damage. Additionally, the packaging should be sealed tightly to prevent air leaks and ensure the cooling material remains effective throughout the shipment.
2. Choose the Right Mode of Transport
The mode of transportation plays a significant role in determining how well perishable goods will be preserved during transit. The two most common modes for shipping perishables are air freight and refrigerated (reefer) trucks or containers.
- Air Freight: Air freight is often the fastest and most reliable option for shipping perishable goods over long distances, especially when dealing with time-sensitive items such as pharmaceuticals or fresh food. Airplanes can maintain stable temperatures throughout the journey, and many cargo holds are equipped with refrigeration units that are ideal for shipping perishables.
- Reefer Trucks/Containers: For ground transport, reefer trucks and containers equipped with refrigeration units are essential. These units can maintain the necessary temperatures, whether frozen, chilled, or ambient, ensuring that the goods remain in optimal condition. Reefer containers are commonly used for shipments that travel by sea, as they provide temperature control during long ocean voyages.
Selecting the appropriate mode of transportation depends on the type of product being shipped, the urgency of the delivery, and the distance it must travel. For example, when shipping high-value items like pharmaceuticals, air freight may be the best option to reduce the risk of product degradation.
3. Plan for Emergency Contingencies
Even with the best planning and precautions in place, unforeseen events such as equipment malfunctions, traffic delays, or extreme weather can disrupt the cold chain. As part of the best practices for shipping perishable items, it’s important to have contingency plans in place to deal with emergencies.
Contingency plans should include backup cooling systems, such as portable refrigeration units, and alternative transportation routes or methods. For example, if a refrigerated truck breaks down in the middle of the journey, having a contingency plan for transferring the shipment to another refrigerated vehicle ensures that the goods will not be exposed to temperature changes during the transfer.
Additionally, businesses should establish communication protocols to ensure that everyone involved in the shipment, from drivers to warehouse staff to recipients, is aware of the situation and can take action if necessary.
4. Work with Experienced Cold Chain Logistics Providers
Shipping perishable goods requires expertise in cold chain logistics to ensure the safe transport and storage of temperature-sensitive products. Partnering with experienced cold chain logistics providers, such as those specializing in refrigerated transport and temperature-controlled warehousing, can help ensure that all aspects of the cold chain are handled professionally.
These logistics providers can assist with packaging, transportation, monitoring, and tracking, making sure that perishables are transported efficiently and arrive at their destination on time and in optimal condition. Additionally, cold chain logistics providers often have access to advanced technologies, such as IoT sensors, temperature-controlled vehicles, and real-time tracking systems, to ensure the highest level of service.
Future Trends in Cold Chain Logistics
As the global demand for perishable goods continues to rise, the cold chain logistics industry is evolving rapidly to meet these challenges. Innovations in technology, sustainability, and global trade dynamics are shaping the future of cold chain logistics, offering businesses opportunities to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and meet changing consumer expectations. Here are some of the key trends that will define the future of cold chain logistics.
1. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Solutions
With increasing global awareness of environmental impact, sustainability is a growing trend in cold chain logistics. Companies are seeking more eco-friendly methods for temperature-controlled transport, such as energy-efficient refrigeration systems, biodegradable packaging, and the use of alternative fuels like electric vehicles and biofuels for refrigerated transport.
For instance, traditional refrigeration units can be energy-intensive and contribute to higher carbon emissions. However, newer technologies such as solar-powered refrigeration systems and low-emission reefer trucks are helping to reduce the carbon footprint of the cold chain process. Additionally, companies are exploring biodegradable or reusable packaging materials to minimize waste, particularly in industries like food and pharmaceuticals where single-use plastics are common.
Sustainability is also being incorporated into warehouse operations. Many companies are investing in energy-efficient temperature-controlled storage solutions, such as warehouses powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, as well as implementing green building certifications to reduce energy consumption.
2. Blockchain Technology for Transparency and Security
As supply chains become increasingly complex and interconnected, there is a growing need for transparency and security in cold chain logistics. Blockchain technology, which provides a decentralized and immutable ledger of transactions, is becoming a popular solution to enhance visibility and traceability in the cold chain.
Blockchain can help ensure that every step of the supply chain, from production to delivery, is recorded and verified. For cold chain logistics, this means that each temperature-sensitive shipment can be tracked in real-time, with all relevant data securely stored and easily accessible. This transparency allows stakeholders to trace the entire journey of a product, ensuring that it has been handled properly and kept within the required temperature range.
Additionally, blockchain technology can help reduce fraud, prevent tampering, and improve accountability in the supply chain. For instance, if there is a temperature breach or delay in the supply chain, the blockchain record will provide a reliable and unalterable trail of events, which can be used to resolve disputes and improve operational efficiency.
3. Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Another exciting development in the future of cold chain logistics is the use of autonomous vehicles and drones for transportation and delivery. Self-driving trucks and drones have the potential to revolutionize the way temperature-sensitive goods are moved across long distances and to remote locations.
Autonomous trucks are already being tested and implemented in certain regions, particularly for long-haul transport. These trucks are equipped with advanced AI systems and sensors that enable them to drive safely without human intervention, reducing the risk of human error, improving fuel efficiency, and optimizing delivery times. These trucks can also be equipped with refrigerated units to maintain temperature-sensitive goods during transit.
Drones are also expected to play a significant role in cold chain logistics, especially for last-mile deliveries. Drones can deliver small, perishable items like medical supplies or food to urban and rural areas quickly and efficiently. With the help of drones, businesses can ensure faster delivery times and better access to customers in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
4. AI and Predictive Analytics in Cold Chain
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming central to predictive analytics in cold chain logistics. These technologies analyze massive amounts of data from IoT sensors, GPS trackers, and monitoring systems to forecast potential issues before they happen.
One key application is predictive maintenance. By identifying patterns in equipment performance, AI can predict when refrigeration units are likely to fail, allowing companies to repair or replace parts before breakdowns occur. This reduces the risk of temperature excursions that could spoil sensitive products.
AI and ML also help optimize routing and supply chain planning. By factoring in historical data, weather conditions, and traffic patterns, predictive analytics can suggest the most efficient routes, reducing delays and ensuring timely delivery.
For example, if data indicates that a specific highway route often causes delays due to congestion, AI can recommend an alternative path to keep the cold chain intact. Similarly, by predicting spikes in demand, companies can allocate resources more effectively and avoid shortages or waste.
Ultimately, AI-driven predictive analytics improves reliability, reduces costs, and enhances the overall resilience of cold chain logistics.
5. The Rise of E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Shipments
E-commerce is transforming industries across the globe, and cold chain logistics is no exception. As more consumers turn to online shopping for perishable goods, the demand for direct-to-consumer cold chain deliveries is expected to rise. This trend is particularly evident in sectors like food delivery, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, where products need to be transported at specific temperatures to maintain their quality.
For example, online grocery shopping has surged in popularity, and customers expect fresh food and perishable items to be delivered directly to their doorstep in pristine condition. To meet these demands, logistics providers will need to develop more efficient and scalable cold chain solutions for e-commerce, including flexible delivery models, smaller refrigerated transport vehicles, and improved last-mile solutions.
6. Global Expansion of Cold Chain Infrastructure
As global trade increases, especially in emerging markets, there is a growing need for cold chain infrastructure to meet the demands of international trade. Cold storage facilities, refrigerated transport systems, and distribution centers are being expanded in regions with rapidly growing economies, such as Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
In these regions, the development of cold chain infrastructure will be essential to maintain the integrity of temperature-sensitive goods, particularly as demand for fresh food, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines rises. International cold chain networks will need to be more interconnected, with the ability to track shipments across borders, ensuring that temperature-sensitive goods are kept within the required ranges throughout the entire journey.
In summary, maintaining an effective cold chain is essential for transporting perishable and temperature-sensitive goods safely and efficiently. With the right technologies and strategies, businesses can ensure product quality while reducing risks and costs. If you’re looking for reliable, budget-friendly solutions for shipping temperature-sensitive items, contact us at ykfreight.com today to streamline your logistics and keep your shipments in optimal condition.





ASK YOUR QUESTIONS